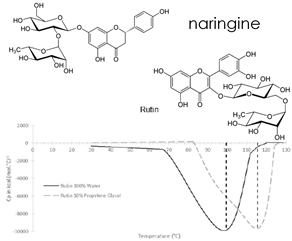
Food flavonoids have a high antioxidant activity and could be very sensitive to thermal degradation. The degradation kinetics, followed in part by DSC microcalorimetry, and the evolution of the antioxidant activity of different model flavonoids, show that the flavonoid degradation depends on the heating temperature and on the structure of the molecule, the addition of propylene glycol ensures a protective effect against the heat treatment. Finally, it seems that the degraded products could have an antioxidant activity equal or sometimes superior to native flavonoids.
Associated publication : Ioannou I, Kriznik A, Chekir L, Ghoul M. Effect of the Processing Temperature on the Degradation of Food Flavonoids: Kinetic and Calorimetric Studies on Model Solutions. J. Food Eng. and Technol. 2019 ; 8(2):91-102.
DOI : 10.32732/jfet.2019.8.2.91
HAL : HAL-02392716